Design Library
Here we present parameters of certain standard components, including screws, nuts, standardoff, retaining rings and bearings.
Screws
We are mainly using M2.5, M3 and M4 screws in our robots.
Socket Hex Screws
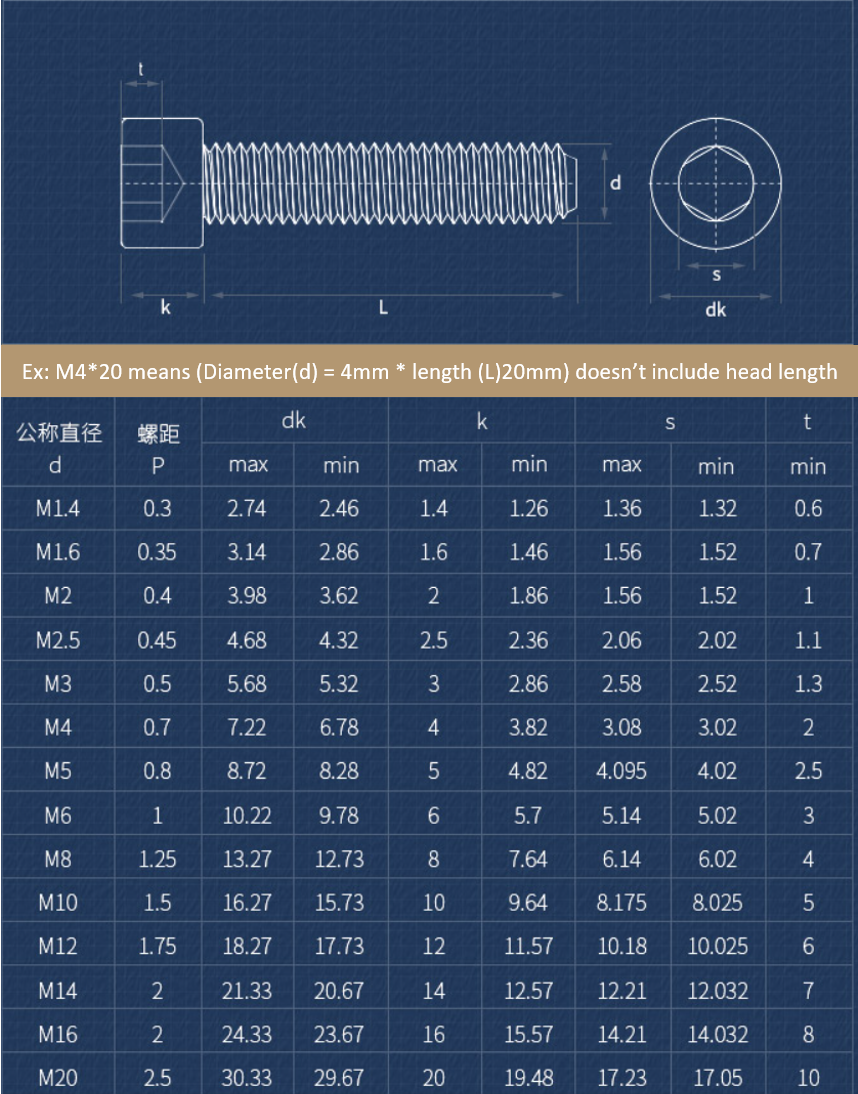
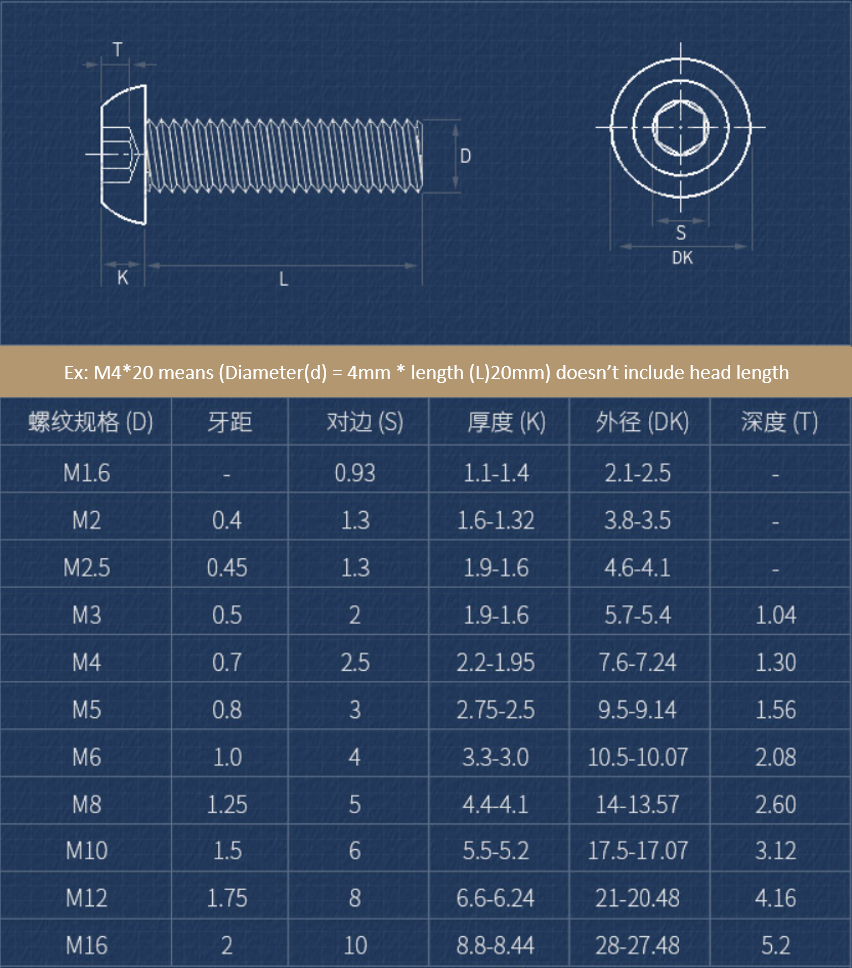
Rounded Head Screws
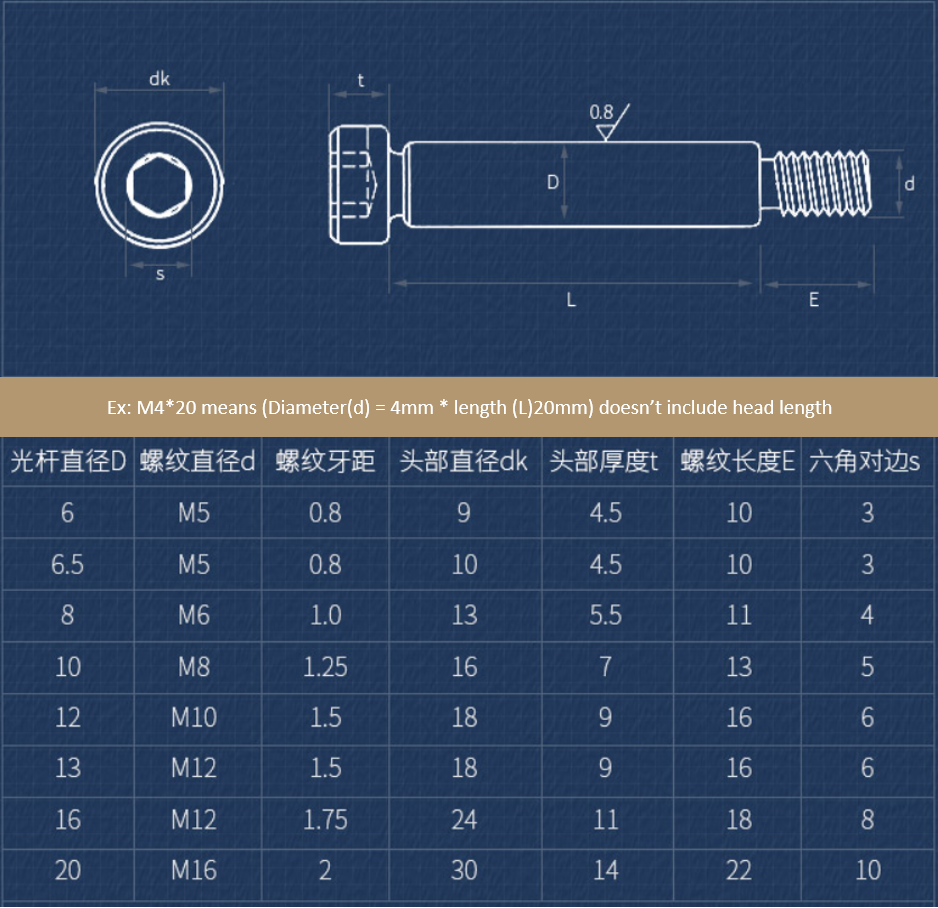
Shoulder Screws
These types of screws consist of integral threads that are present on half or less of the screw shank and the rest of the shaft is enlarged and smooth to allow the bolted material the ability to rotate or move around the screw axis. Much like all other screws, shoulder screws are meant to hold objects together and in a particular position. However, these screws are designed for use in parts which requires a mounting pin, joint, shaft, dowel, pivot, or sliding motion. Items such as:
- Bearings
- Bushings
- Machinery support
- Motion guiding
- Precision spacing
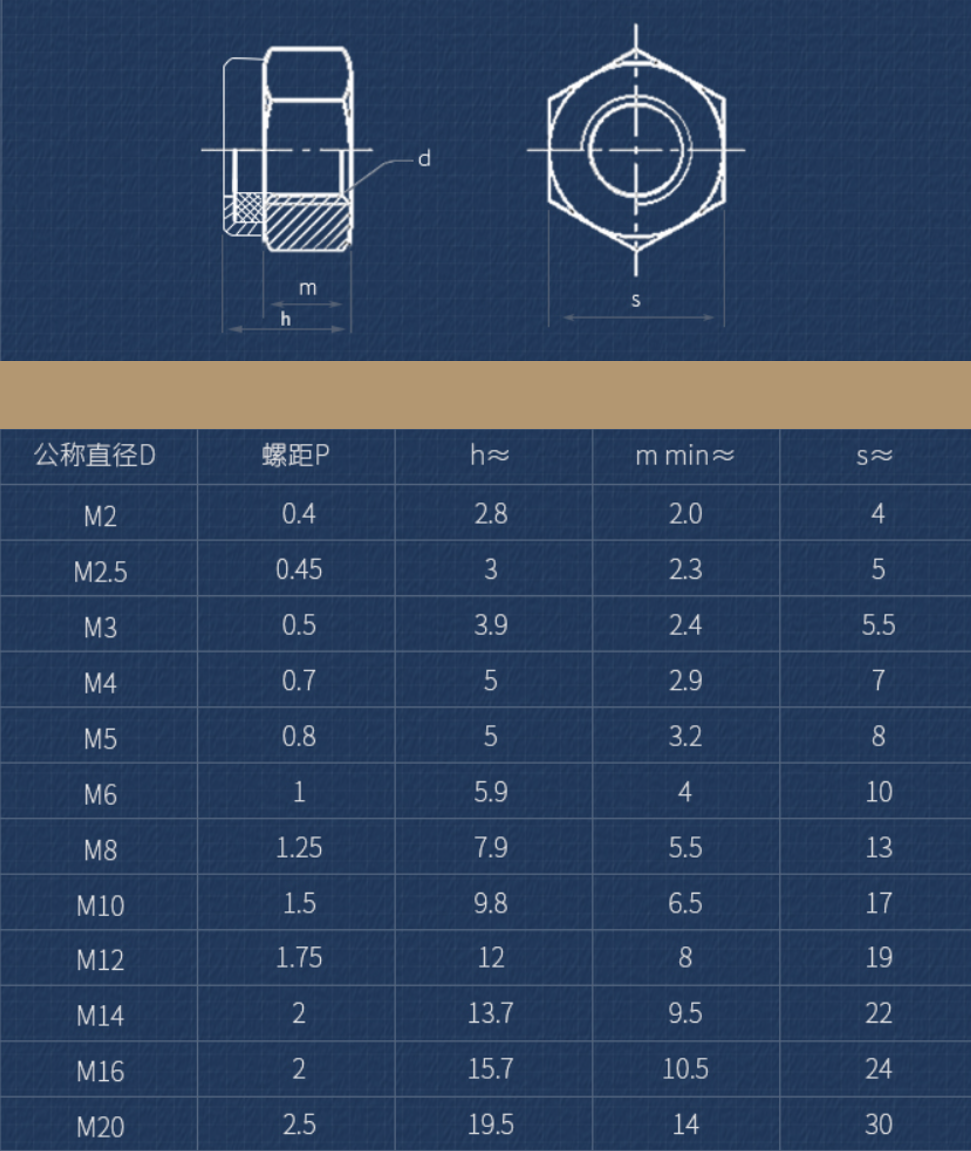
Nuts
To make sure the fastening of the each part on the robot, we only use the Nylon-Insert Locknuts. a nylon collar is placed at the end of the nut that increases friction on the screw thread. The screw thread does not cut into the nylon insert, however, the insert deforms elastically over the threads as tightening pressure is applied. The insert locks the nut against the screw as a result of friction, caused by the radial compressive force resulting from the deformation of the nylon.
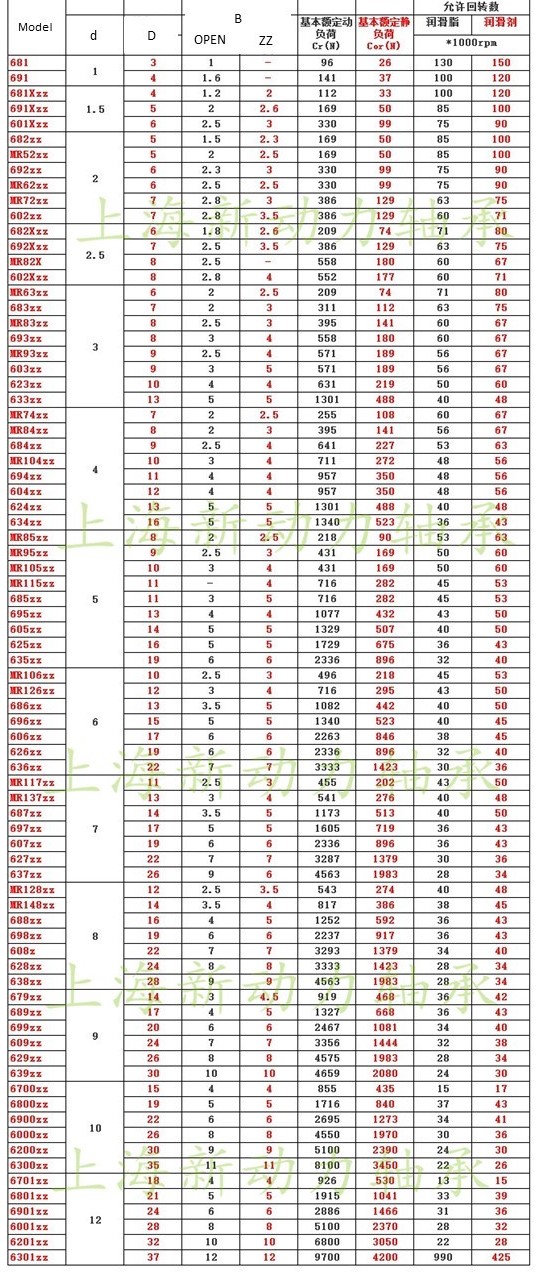
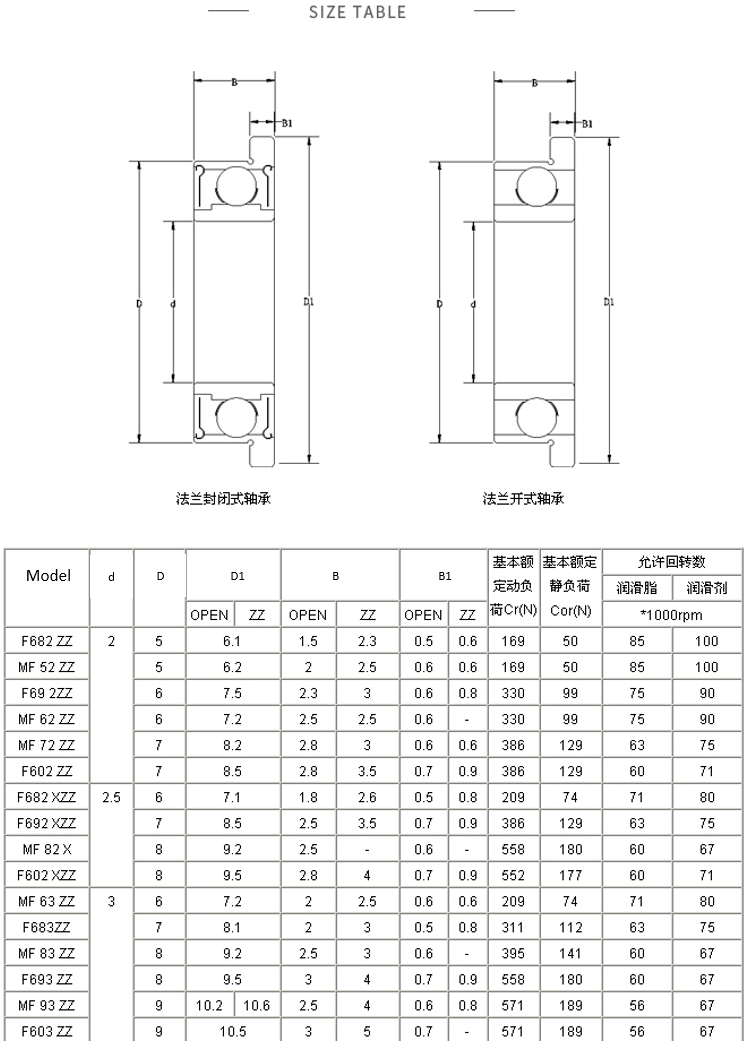
Bearing
Mini Flange Bearing
The inner diameter from 2mm to 9mm
- d: inner diameter
- D: outer diameter
- D1: flange diameter
- B: bearing thickness
- B1: flange thickness
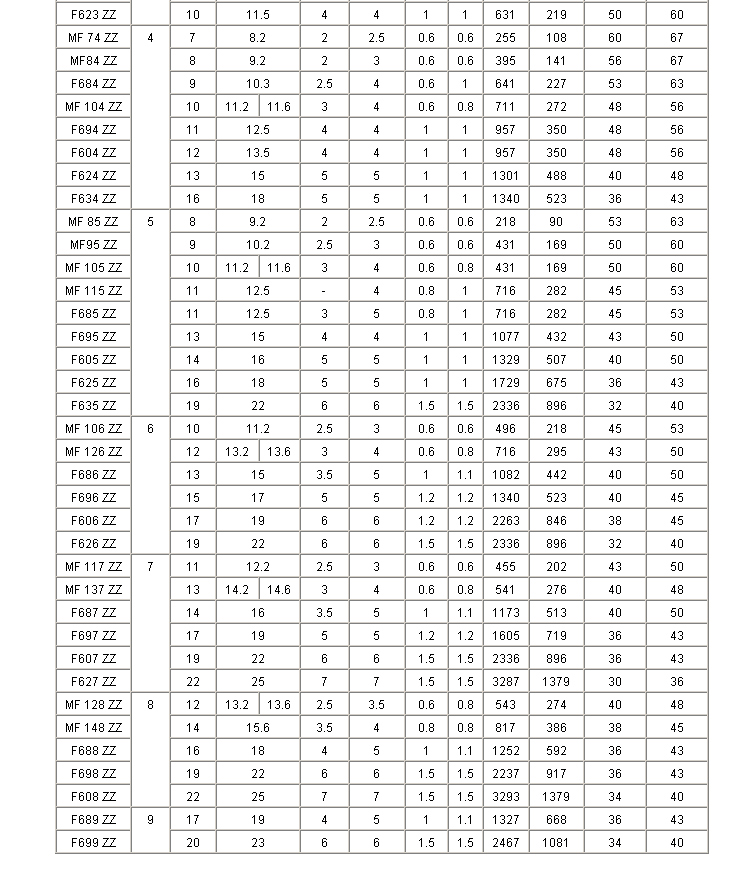
Mini Deep-groove Bearing